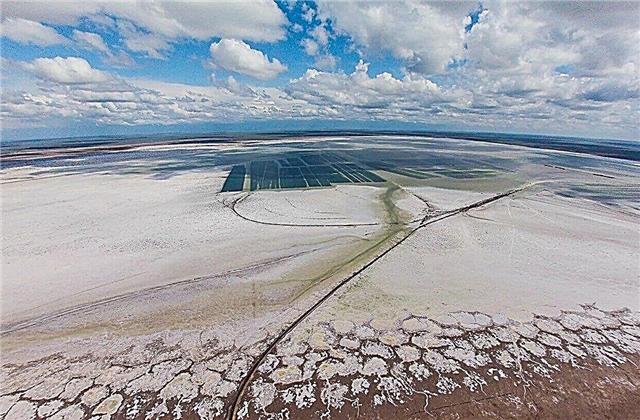
Salt lakes are found throughout Russia. Over time, the proportions of substances can change under the influence of various factors. According to the degree of mineralization, the lakes are subdivided into brackish, salty and saline. Salt lakes are formed in different ways, for example, some in the past were sea bays or salt pits.
Sometimes they dry up, leaving deposits of deposits on the surface, but in a favorable season for themselves, they are again filled with water. The depth is also rarely great, although there are exceptions. The advantage of such lakes for tourists is medicinal and cosmetic mud. In most cases, you can use mud without a doctor's prescription, but it is better to consult a specialist. It is not surprising that sanatoriums and recreation centers have been built on the shores of many lakes.
Salt lakes - analogs of the Dead Sea in Russia
List of the country's most popular salt lakes for recreation and treatment.
Baskunchak
Salt lake of the Astrakhan region. Area - 106 km², maximum depth - 3 meters. Geographically, it is part of the Bogdinsko-Baskunchaksky Reserve. There are deposits of healing clays and muds. The brine is used for taking baths. Salt deposits are visible to the naked eye. A sanatorium of the same name was built on the coast. The best time to visit is summer. There are two tourist routes that go around the lake.

Elton
Located in the Volgograd region near the border with Kazakhstan. The area is 152 km². This is the largest salt lake in Russia. The depth varies significantly depending on the season, but does not exceed the limit of one and a half meters. The concentration of salts is so high that they precipitate. Mineralization is one of the highest in the world. There is a balneological resort on the shore that uses local mud, and in the village nearby there is a sanatorium "Elton".

Koyashskoe
Lake on the southern coast of the Kerch Peninsula. The area is slightly more than 5 km², the average depth is less than a meter. Koyashskoye is separated from the Black Sea by a narrow isthmus. Salt water is pink in color, which changes in color throughout the year. The phenomenon is explained by the presence of brine and aquatic vegetation. Salt deposits are clearly visible on the stones. It is part of the Opuksky Nature Reserve. These places are most picturesque in May.

Collapse
The lake appeared in the Orenburg region as a result of the flooding of a salt pit. The modest 6.8 hectares are complemented by an impressive maximum depth of 22 meters. Water is considered curative, especially useful for people with skin problems. The salt concentration is comparable to that of the Dead Sea. This prevents the formation of an ice crust even in severe frosts. In the past, Razval had the status of a natural monument.

Bolshoe Yarovoe
Located in the west of the Altai Territory. The area is up to 70 km², the maximum depth is up to 8 meters. Since the food is snowy, the sizes vary at different times of the year. The salinity of the water decreases over the years. At the same time, the chemical composition is still comparable to the Dead Sea. Since 1972, a sanatorium has been operating near the coast, using silt mud and brine for medical procedures.

Vats
The largest lake in Western Siberia belongs to the territory of the Novosibirsk region. The area is up to 2269 km², the maximum depth is 10 meters. Vats are a system of streams that are connected by shallow water areas and channels. There are about 70 islands. In terms of tourism, it is popular as a place for fishing and hunting for waterfowl. Recreation centers operate on the shore. The Kirzinsky reserve has been created in the north of the lake.

Sasyk-Sivash
The largest lake in Crimea. The area is over 73 km², the maximum depth is 1.2 meters. Separated from the sea by an isthmus. Salt and sea sand are mined on this strip of land. The color of the water is pink, in some seasons it becomes even more saturated, turning into red. Bubbling on the surface - salt water emissions. Mud is used for medical procedures, and algae in cosmetology.

Big Yashaltinskoe
Located in the Republic of Kalmykia. Area - 40 km², average depth - half a meter. The lake can be called shallow, which is explained by the structure of its almost flat bowl. Belongs to the Manych lake group. In the summer months, there are many vacationers here, but mostly locals. The healing mud and well-warming water potentially give hope for the development of the tourism industry here.

Saki
One of the most popular lakes in Crimea. The area is 9.7 km², the average depth is a little more than half a meter. It is separated from the Black Sea by a strip of land. The western part is a raw material base, the eastern part is a recreational one. The local black ooze is used to treat hormonal problems, skin infections and other diseases. 15 sanatoriums have been built in the district. The most famous are named after Budenko and named after Pirogov.

Dus-Khol (Svatikovo)
Located in the central part of Tuva. The translation of the name is "salt lake". The area is 55 hectares, the average depth is 2 meters. The coast is actively used for recreation in the warm season. There are a lot of visitors, so the infrastructure is gradually developing. A cafe was built in the form of a yurt with appropriate decoration. There are sanatoriums, camping, places for setting up tents. The brine and mud are used for all kinds of treatments.

Salt (Zavyalovskie lakes)
330 lakes are located on an area of 220 thousand hectares in the Altai Territory. Among them is Salty, rich in deposits of mud and mineral waters. Silt deposits have different colors and properties. The entrance to the water is not convenient everywhere, as tourists dig holes near the shore for mud extraction. There is a recreation center called "Salt Lake". There is parking, places for tents, small shops, rental houses.

Kak-Hol
Belongs to the territory of Tuva. The translation of the name is "swampy lake". The area is 2.2 km², the maximum depth is slightly more than half a meter. You won't be able to swim here - the water is shallow. But tourists come for mud therapy, smear themselves with silt right on the shore of the reservoir. There is little vegetation around, salt marshes, salt deposits and small swamps. Nearby attraction is Dus-Khol lake.

Kiranskoe
It is located in Buryatia and has a more common name - "Salty". Area - 0.4 km², maximum depth - 1 meter. The volume of water changes not only in different months, heavy rain can significantly affect the surface area. Exploration of the lake began in 1700. Now the most popular institution here is the Kiran mud bath. In 1980 it received the status of a natural monument.

Khadyn
Salt lake in Tyva. The name translates as "birch". The area is 2.3 thousand hectares, the average depth is 2 meters. The river of the same name flows in. The shores are dark with distinct white stripes - salt deposits. Due to the mineral composition of the water, fish are not found here, and there are also few insects and birds. Mud and water can be used to treat and prevent disease, but tourism is still underdeveloped.

Ebates
The largest salt lake in the Omsk region. The area is up to 11 thousand hectares, the maximum depth is 2 meters. Sizes are variable, depending on rainfall and season. Despite the high mineralization and large deposits of medicinal mud, there are no clinics and recreation centers. Tourism is wild, there are not many visitors. There is a constant collection of crustacean cysts. Since 1979, the reservoir has been declared a natural monument.

Salty
Located in the Krasnodar Territory, near the village of Veselovka. Until the 50s of the last century, salt was mined here. The mud lies at the bottom in layers, you can easily fall ankle-deep. Procedures should not be carried out longer than 15 minutes. Tourists wash off the dried crust usually in the sea, since the beach is within walking distance. Nearby are the mud volcanoes Hephaestus and Tizdar.

Kulundinskoe
The largest lake in the Altai Territory.The area is 728 km², the maximum depth is 4 meters. The banks are relatively smooth and flat, with the exception of the eastern part. There are many islands, bays, ragged lines. On the east side, there are many comfortable sandy areas for recreation. Residual reservoir - formed after the shallowing of a large lake basin.

Bulukhta
Located in the Volgograd region. The translation of the name is "spring", also called Bitter-Salty. The area is 77 km². The banks are indented, partly swampy, there is a layer of Glauber's salt. The muddy bottom is uneven, you can fall through. The largest of the islands was named Small. There are rare species in the area, for example, the burial eagle. Nearby attraction: Lake Elton.

Tambukan
It is part of two constituent entities of the Russian Federation at once: the Stavropol Territory and Kabardino-Balkaria. Pyatigorsk is only 9 km away. The area is 170 hectares, the average depth is 2 meters. The composition of the mud is comparable to that of the Dead Sea deposits. You cannot drink water, it will cause health problems, but swimming is allowed, only for a short time. There are no fish, as well as nesting places for birds. Tourists are repelled by the unpleasant smell emanating from the Tambukan.

Raspberry
Located in the Altai Territory. The area is 11.4 km². A tourist base has been built on the coast. Since 2013, the reservoir has been included in the "Big Tourist Golden Ring of the Altai Territory" - a popular tourist route. The healing mud deposits attract those wishing to carry out wellness procedures. Temperature drops happen all the time, this must be taken into account when planning a trip.

Bearish
Refers to the Kurgan region. Area - 61.3 km², maximum depth - 1.2 meters. The increased salinity and mineralization of the water caused the lack of fish and aquatic vegetation. The lake is divided into Big and Small by six islands. A resort of the same name was built on the coast. Mud is used for treatment, as a preventive measure and to raise the general tone of the body.

Khan
Salt Lake of the Krasnodar Territory. The area is 86 km², the maximum depth does not even reach a couple of meters. In the past, the reservoir was the gulf of the Azov Sea. Periodically dries up, exposing salt crusts. Due to the healing properties of the mud, it was taken under protection. The sanatoriums of the city of Yeisk use local silt deposits in a wide range of procedures. Since 1988 it has the status of a natural monument.

Party
Bitter-salt lake of Khakassia. Area - 2.6 km², maximum depth - 2 meters. The reservoir is gradually desalinated. Salt does not completely dissolve in water, which results in a crusty precipitate at the bottom. There are tourist bases, including "Voskhod". The area is considered a resort of regional importance. Nearby attraction - object of cultural heritage "Tus Burial".

Bitter
Located in the Novosibirsk region near the village of Novoklyuchi. The area is just under 7 km². The northern coast is more suitable for recreation. Mud deposits have high characteristics in terms of mineral composition. They are black, oily with a distinct smell of hydrogen sulfide. Here they treat skin diseases, nervous system, respiratory organs and more. The health-improving complex of the same name works.

Ulzhai
Located in the south-east of the Omsk region. The area is 14.5 km², the maximum depth is 1.3 meters. The northern coast is "multi-layered", the terraces hang over each other. It is more convenient to enter the water from other sides. The thickness of the layer of local mud deposits exceeds half a meter. They are useful in the treatment of many diseases. They are used, among other things, at the Omskiy Rehabilitation Center. In 1978 it received the status of a natural monument.

Tinaki
Salt lake a few kilometers from Astrakhan. The name is derived from the silt deposits, which are called mud in the district. The pink color of the water is due to the presence of magnesium salts. The area is small, the depth in summer is no more than a meter. A mud cure resort has been built on the shore, and a rehabilitation center of the same name is also operating. People come here not only for treatment, but also for cosmetic procedures.

Botkul
Located on the border between Russia and Kazakhstan. The area is up to 70 km². The reservoir is shallow, periodically dries up. Salt deposits and areas with mud deposits are clearly visible on the surface. There is a strong smell of hydrogen sulphide in the area, and the territory is covered with salt marshes. There are prospects for the development of several directions of tourism, but so far the potential has not been practically realized.

Chokrak
Crimean salt lake near the village of Kurortnoye. The translation of the name is "spring". The area is 8.5 km², the average depth is less than a meter. It is separated from the Sea of Azov by an embankment. The water is pink in color, its saturation is variable. Sediments and miniature crustaceans gave such a hue. Muds are useful in cosmetology and treatment. The composition of the water is close to that of the Dead Sea. The lake is part of the reserve.

Bitter
Salt lake in the Yegoryevsky district of the Altai Territory. The area is a little less than 42 km², the average depth is 3.5 meters. The banks are low with a convenient entrance to the water, with the exception of the northern side, where a swamp has formed. The channel connects the reservoir with the Gorko-Peresheechnoye lake. The Lebyazhye sanatorium has been operating on its banks for a hundred years, using local mud and mineral waters for procedural treatment. The composition of the water is comparable to that of Essentuki 17.

Moinak
Crimean lake, located in the west of Evpatoria. The area is 1.76 km², the maximum depth is less than a meter. The territory is considered a resort in every sense. There are comfortable beaches on the east coast. Sludge and mud are used for cosmetology and treatment. The water contains beneficial minerals. There are several sanatoriums, the most popular is the Moinakskoye mud bath.